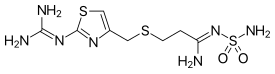
Famotidine is a non FDA-approved non-prescription medicine commonly recommended by vets to control the release of stomach acid in dogs. Scientifically speaking, Famotidine is a histamine receptor-2 blocker that helps to reduce the amount of stomach acid being naturally produced.
Purposes of Famotidine
Famotidine is recommended in a variety of gastric related issues, the main ones of which are listed here.
- It plays a major role in healing stomach and intestinal ulcer and preventing further formation of the same. Ulcers tend to cause significant damage to the linings of the stomach, small intestine, and even the esophagus.
- Subsequently it can also effectively treat gastritis and acid reflux, which can severely affect the esophagus.
- More specifically, it is useful in the treatment of uremic gastritis, drug induced or stress related ulcers and gastritis, heartburn, and esophageal reflux.
- It is also useful in treating stomach inflammation of the stomach due to kidney failure.
- Mast cell tumors lead to the creation of large amounts of secretion of histamine, which can be treated with Famotidine.
How does Famotidine function?
Gastric acid is secreted due to the stimulation of the H2 receptors present in the membranes of stomach cells. Primarily an anti-ulcer drug, Famotidine blocks these H2 receptors by binding to the lining of the stomach and thus moderating the secretion of gastric acid. This is how the ulcers are healed and further ulcers are stopped from growing worse.
How is Famotidine administered?
Famotidine should not be used without the recommendation of the vet, and you should always follow the directions of use specified by them. If the directions of use are unclear then clarify them or ask the pharmacist any doubts you may have.
Usually the dosage is 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg per pound of the dog’s body weight, to be given twice a day. Having said that, this is not uniformly true for all dogs and will vary according to breed, degree of illness, medical history, and other factors. Stick to the dosage advised by the vet. Always keep in mind that this drug should not be given along with food. It may also be available in the form of liquids or suspensions.
In case you miss a dose then give it to your dog as soon as you remember. However if this happens to be too close to the next scheduled dose then skip it and return to the original routine. Do not give two doses together or overdose. Overdosing with famotidine is not fatal thankfully, but it may cause other symptoms such as vomiting, paleness, increased heart rate leading to collapse, or just restlessness. If you have overdosed by mistake then contact your vet immediately.

Potential side effects
Usually this is a relatively safe drug that does not cause lasting side effects. You must however be aware of all the probable negative reactions to stay prepared, and possibly prevent them if you can. Following points are the possible side effects of this drug.
- Any kind of allergic reaction indicates that you must stop giving this medicine at once. These reactions include swelling of the lips and mouth region (including the face and the tongue), formation of hives, and breathlessness.
- Unexplained tiredness, drowsiness and loss of appetite have also been known to occur after taking this medicine.
- Headache accompanied by diarrhea also takes place sometimes. For some dogs this might cause the opposite side effect of constipation.
Reactions of this drug may take various forms, so if you notice any behaviour or affliction out of the ordinary after taking the medicine, contact your vet at once. Such occurrences are quite rare because this drug is a safe one and thus widely recommended by vets.
Risks and Precautions to bear in mind
- Although the drug is often sold as over the counter medication, never use it without first consulting your vet. Start using the drug on their advice and stop the treatment if and when they ask you to.
- Use the medicine with caution and avoid overdosing at all costs if your pet has a history of heart, liver, stomach cancer, and kidney diseases, or if they are pregnant. Your vet may also think it safer to avoid this drug if your dog is nursing.
- If your dog has any of the above conditions discuss it at length with your vet to figure out if it is safe for your dog to ingest.
- Never give the drug along with food as it reduces the effectiveness of the medicine.
- You may store Famotidine at room temperature, but keep it away from direct sources of light and moisture.
- This drug should not be used for dogs with allergies or hypersensitivity.
- Drug interactions have been known to happen with certain kinds of antacids, digoxin, ketoconazole, and metoclopramide. If your pet is on any of these medicines then be sure to space out the intervals by giving them the famotidine a couple of hours before or after giving them these medicines.
- A bad reaction has been known to happen when this drug interacts with azathioprine, since it leads to rapid loss of white blood cells. In case your dog has to take medicines which may interact with famotidine your vet is likely to recommend taking vitamins, probiotics, and other dietary supplements.
Famotidine is thus a very commonly used drug that can treat a large variety of gastrointestinal diseases and infections. A great advantage is how applicable and effective this is for almost every dog breed and how easily it can be acquired at the pharmacy. That does not mean however that it can be used at will whenever any stomach issues are visible.
The multifaceted nature of this drug is one of the main reasons for its popularity. Although it is mostly used to cure and prevent complications of stomach ulcers, it has been known to cure many other ancillary gastric related problems while treating the ulcer.
Famotidine is affordable, effective, widely available at medical stores, and brings quick results. It is thus the first preference of several veterinarians across the globe.
Table of Contents





